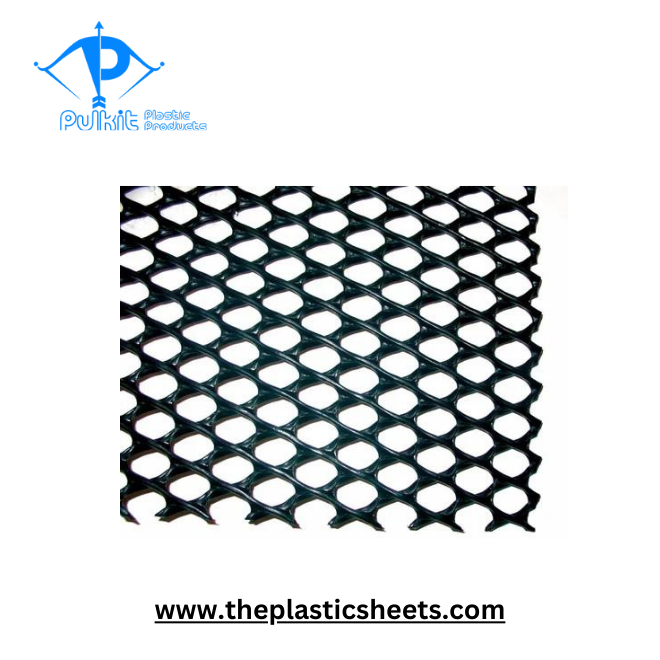
In the world of civil engineering and environmental management, innovation plays a key role in the development of materials that enhance the safety, stability, and efficiency of various projects. One such material that has gained significant attention in recent years is geonet. Although it may not be as well-known to the general public, geonet plays a vital role in a wide array of applications, particularly in environmental engineering, drainage systems, and construction. In this article, we will explore what geonet is, its benefits, applications, and why it is becoming an indispensable component in the modern engineering world.
What is Geonet?
A geonet is a type of geosynthetic material designed to facilitate drainage and filtration in various construction and environmental applications. It is typically made from polymeric materials Pulkit Plastic Products such as polyethylene (HDPE), which are woven or extruded into a net-like structure. This network of interconnected polymer filaments creates a three-dimensional matrix that allows for excellent drainage performance. Geonets are commonly used in situations where water drainage and filtration are crucial, such as in landfills, road construction, and slope stabilization projects.
The key feature of a geonet is its open structure, which allows water to pass through the material while filtering out larger particles and debris. This makes geonets an essential part of geosynthetic drainage systems, which are used to direct water away from structures, prevent waterlogging, and maintain soil stability.
Types of Geonets
Geonets come in various configurations to suit different applications. The primary types include:
-
Uniaxial Geonets
Uniaxial Geonet in road construction are manufactured by extruding polymeric filaments into a single direction, creating a structure that provides drainage along a single axis. These geonets are often used in applications where drainage is needed in a specific direction, such as under roads or as part of a sub-surface drainage system. -
Biaxial Geonets
Biaxial geonets, on the other hand, have filaments extruded in two directions, creating a mesh-like structure that offers multidirectional drainage. These geonets are particularly useful in applications where water needs to be drained from multiple directions, such as in landfills, retaining walls, or slope stabilization systems. -
Geo composites with Geonets
Geo composites combine geonets with other geosynthetic materials, such as geotextiles or geomembranes, to create an integrated drainage solution. These geo composites offer additional benefits such as increased filtration, separation, and protection, making them ideal for more complex applications like landfill caps, road construction, or retaining wall systems.
Benefits of Geonets
-
Effective Drainage
One of the primary advantages of using geonets is their ability to provide efficient drainage in a wide range of applications. The three-dimensional structure of the geonet allows for the quick movement of water, ensuring that excess moisture is effectively channeled away from structures and systems that require protection. This is particularly important in areas prone to heavy rainfall or in projects where water accumulation could damage the integrity of the structure, such as roads or foundations. -
Cost-Effective Solution
Geonets are a cost-effective solution for drainage and filtration. They are typically less expensive than traditional drainage systems that rely on gravel, pipes, or other materials. The simplicity of geonets, combined with their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements, makes them an attractive choice for contractors and engineers working on large-scale projects. -
Durability and Longevity
Geonets are made from high-quality, durable materials such as HDPE, which are resistant to degradation from UV radiation, chemicals, and environmental factors. This means that geonets can withstand harsh conditions over long periods, providing long-term performance without the need for frequent replacements. This durability makes them an ideal choice for use in harsh environments, such as landfills, where the material must perform reliably for decades. -
Environmental Benefits
Geonets play a crucial role in environmental engineering, particularly in waste management and erosion control. They help manage stormwater runoff, reduce soil erosion, and prevent contamination from leachate in landfills. By facilitating proper drainage and filtration, Geonets for highway construction ensure that water does not seep into the ground, which can lead to pollution of surrounding water sources. Additionally, the materials used to create geonets are often recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly construction process. -
Versatility
Geonets are highly versatile and can be used in a variety of applications, including soil stabilization, drainage, filtration, and erosion control. They can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a project by choosing the appropriate type of geonet (uniaxial or biaxial) and combining them with other geosynthetics, such as geotextiles or geomembranes. This flexibility makes geonets a go-to solution for a wide range of civil engineering and environmental applications.
Applications of Geonets
-
Landfills
One of the most common applications for geonets is in landfills, where they are used as part of a leachate drainage system. Geonets are placed between layers of soil or geomembranes to channel leachate (the liquid that percolates through waste) to collection points. This helps prevent the contamination of surrounding groundwater and ensures that the landfill operates efficiently. Additionally, geonets are used to manage stormwater runoff and prevent erosion in landfill areas. -
Road Construction
Geonets are widely used in road construction to improve drainage systems. They are placed beneath roads and highways to direct water away from the surface and prevent waterlogging. This helps improve the longevity of the road by reducing the risk of soil erosion and preventing damage caused by moisture accumulation. Geonets are also used in sub-surface drainage systems for highways and railways to improve stability and load distribution. -
Slope Stabilization
In projects involving steep slopes, geonets are used to prevent soil erosion and enhance slope stability. The geonets help maintain the integrity of the soil structure by facilitating water drainage and preventing water from accumulating on the slope. By reducing water pressure and improving soil cohesion, geonets help prevent landslides and other forms of soil displacement, which can be a significant risk in mountainous regions or areas with unstable soil. -
Retaining Walls
Geonets are also used in the construction of retaining walls, where they serve as a drainage layer to prevent water pressure from building up behind the wall. This helps to prevent wall failure due to water accumulation, which can lead to cracks, bulging, or even collapse. Geonets ensure that water is effectively channeled away, reducing the likelihood of structural damage and prolonging the lifespan of the retaining wall. -
Erosion Control
Geonets are used in erosion control projects to protect soil from being washed away by water. Whether it’s along riverbanks, coastal areas, or construction sites, Geonet use in road engineering help control the movement of water while allowing soil particles to stay in place. The open mesh structure prevents excessive runoff and reduces the risk of erosion, ensuring that the landscape remains stable.
Conclusion
Geonets are an essential part of modern engineering and environmental solutions, providing effective drainage, filtration, and stabilization. With their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness, they offer significant benefits across a wide range of industries, including landfill management, road construction, slope stabilization, and erosion control. As the demand for sustainable and efficient solutions grows, geonets are likely to remain a key material in both civil engineering and environmental protection, ensuring the safe and effective management of water and soil in various projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between geonets and geotextiles?
Geonets and geotextiles are both types of geosynthetics used in civil engineering, but they serve different purposes. Geonets are primarily used for drainage and filtration due to their three-dimensional structure, which allows water to flow through them while filtering out particles. In contrast, geotextiles are fabric-like materials used for separation, filtration, reinforcement, and stabilization in various applications. While both materials may be used together in some projects, their functions are distinct.
2. Can geonets be used in both wet and dry conditions?
Yes, geonets are designed to function effectively in both wet and dry conditions. They are particularly useful in wet environments where drainage is necessary to prevent water accumulation. Geonets are resistant to water damage and can maintain their structural integrity in high-moisture environments, such as landfills or drainage systems.
3. Are geonets environmentally friendly?
Yes, geonets are considered environmentally friendly due to their ability to control water runoff, reduce erosion, and prevent contamination. Many geonets are made from recyclable materials like HDPE, which helps reduce environmental impact. Additionally, they help protect natural resources by preventing leachate from polluting groundwater.
4. How long do geonets last?
Geonets are highly durable and can last for several decades, depending on the environmental conditions and application. They are resistant to UV radiation, chemical degradation, and wear, making them an ideal choice for long-term applications such as landfills, roads, and slope stabilization.






Leave a Reply