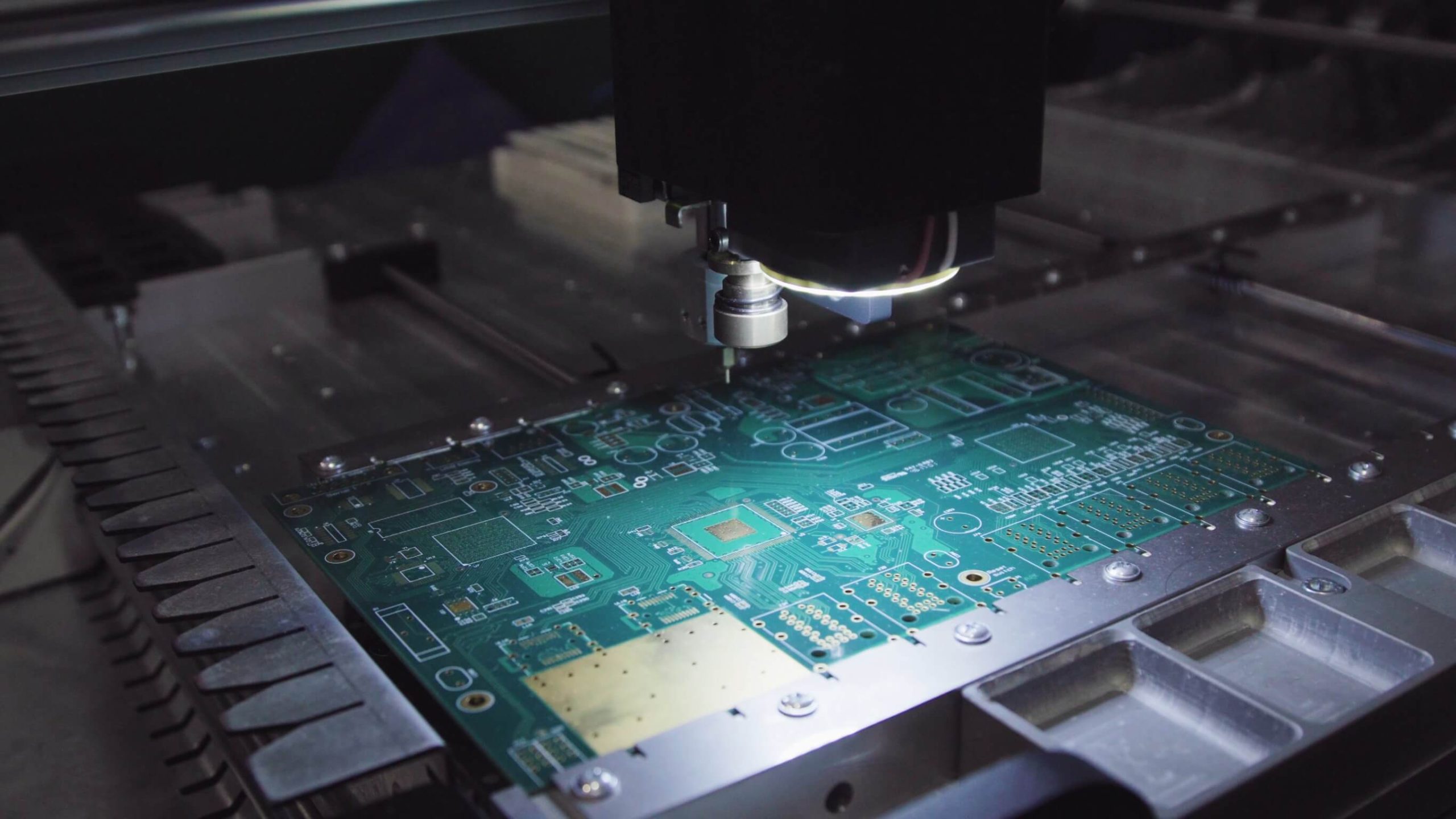
Printed circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronics, driving everything from smartphones to industrial machines. Though end-users often do not pay much attention to these complex components, the assembly process is an extraordinary technological feat. The process, known as printed circuit board assembly or PCBA, has seen a wave of innovations aimed at improving efficiency, precision, and overall product quality.
What is Printed Circuit Board Assembly?
PCB assembly is the process of attaching various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits onto the PCB. This transforms a blank board into a fully functional unit capable of performing specific electronic tasks. The two main technologies involved are Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT):
- In SMT, components are soldered straight onto the printed circuit board surfaces, which benefit it for smartphone or wearable-device design.
- However, THT involves drilling through holes so components may pass by. It tends to be solid in mechanical holding due to components passed through in it. Mainly, they apply it when components are installed for heavy equipment usage, in machines, etc.
Phase involved in this process are;
- Application of solder paste – Applied a paste at one end so the components connected together.
- Component Placement – High-speed automated machines place components onto the board.
- Soldering & Inspection – Components are soldered into place, followed by quality checks to ensure reliability.
While these basics remain the same, the way PCBs are assembled has undergone a sea change in the recent past.
New Advancements in PCB Assembly
Advancements in PCBA are solving traditional challenges such as manufacturing inefficiencies, product defects, and environmental impacts. The following are some of the most important innovations that propel the industry forward.
- Advanced Automation and Robotics
Automation has long been part of PCB assembly. Modern robotics just takes it one step further: Systems equipped with AI-driven vision technology can identify and place components with a precision of one micron, greatly reducing errors. The machines can also dynamically adjust to design changes, thus keeping downtime during the transfer of production at a low level.
- 3D Printing in Electronics Manufacturing
One of the innovative applications of PCBA is 3D printing, which directly prints multilayer circuit boards. Traditional PCB manufacturing involves several etching, layering, and drilling steps, which are very time-consuming and wasteful. With 3D printed circuit boards, fabrication teams can print personalized designs much faster, saving up to 70% in lead times.
- Innovative Techniques for Soldering
Soldering, the process of melting solder to join components to the PCB, is changing with innovations in laser soldering. This technology replaces traditional wave or reflow soldering. Laser systems provide pinpoint accuracy with minimal heat dissipation, making them ideal for fragile surfaces like flex PCBs used in medical implants and foldable smartphones.
Laser soldering also ensures quality control, since it delivers energy in milliseconds that is accurately measured. This results in reducing defects such as bridging-where excess solder bridges separate components-or overheating delicate parts.
- Clean-Tech Manufacturing Processes
With the rising trend of sustainability, PCB manufacturers are now switching to eco-friendly alternatives. In most traditional PCBA processes, hazardous chemicals and high power usage are involved. Nowadays, with the use of water-based fluxes and lead-free solders, toxic materials are being replaced to make workplaces safer and more environment-friendly.
In addition to materials, most factories are adopting energy-efficient robotics and AI-managed production in a bid to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Embedded Components Technology
Manufacturers now mount some passive components, like resistors or capacitors, directly into the board layers rather than mounting all the components on the PCB surface. This reduces the weight and footprint of the final product and makes it highly useful for applications in which space constraints are critical, such as in aerospace technology or 5G-enabled devices.
Secondly, the incorporation of technology increases robustness through the reduction of mechanical stress on parts, which is essential in ruggedized designs of industrial applications.
- Real-Time Data Analytics and Quality Control
Factory IoT (Internet of Things) and AI-driven analytics are changing the face of quality control. Machines perform high-speed optical inspections at the time of assembly and utilize real-time data to identify defects at each step of the manufacturing process.
This feedback loop allows manufacturers to identify areas of failure so that adjustments can be made proactively before they become critical issues.
Conclusion
Such innovations in printed circuit board assembly pave the way for far more reliable, sustainable, and efficient electronic devices. With the effortless integration of robotics and groundbreaking processes friendly to the environment, new improvements are underway and affecting automobile, healthcare, telecommunication, and consumer electronics.
For organizations, redefining manufacturing processes should not only incorporate the latest advancements of PCB assembly; it is essentially an investment to ensure efficiency to produce high quality, future-proof products that should meet the ever-changing demands in the modern world.
Whether in a growing start-up designing the smartest possible devices or just an established player in systems of industry, staying ahead on PCBA technology will give for better cost, faster time, and more than satisfied end users.






Leave a Reply